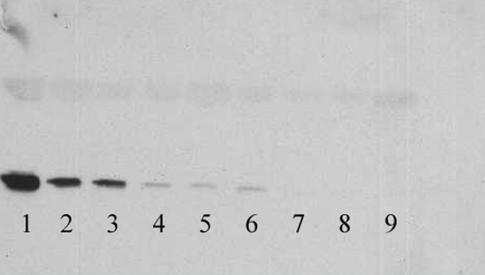
CSF 14-3-3 Western blot
Method
| SDS-PAGE gel | 12% SDS-PAGE running gel with 4% stacking gel |
|---|---|
| CSF volume | CSF volume: 15μl of CSF sample per well |
| Electrophoretic conditions | 40mA constant current for 1 hour 20 minutes |
| Transfer conditions | 0.72mA/cm2 gel for 2 hours |
| Primary antibody |
Mouse monoclonal anti-14-3-3β (Santa Cruz Code: sc-1657) 1:1000 dilution incubated overnight |
| Secondary antibody |
rabbit anti-mouse Ig HRP (DAKO Code: 1: 1000 dilution for 1 hour |
| ECl reagent | ECL Plus (GE Healthcare Code: RPN2132) |
| Exposure time | 2 minutes |
Results
Lanes 1, 2, 3 are positive for CSF 14-3-3
Lanes 4, 5, 6 are weakly positive for CSF 14-3-3
Lanes 7, 8 and 9 are negative for CSF 14-3-3
Lanes 1 and 2 are from two patients with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)
Lanes 3 and 4 are from patients who have had a stroke
Lanes 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 contain CSF samples from patients who do not have CJD
In the United Kingdom weakly positive CSF 14-3-3 results are not considered to be supportive of a diagnosis of sporadic CJD.
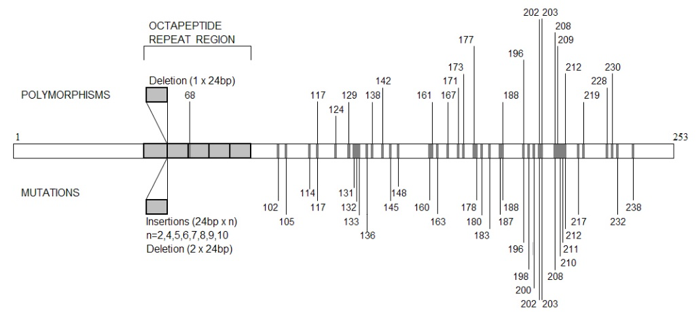
Genetics
PRNP: Human prion gene variation showing positions of non-pathogenic polymorphisms, and pathogenic mutations. (The codon numbers are shown.)
Genetics 2
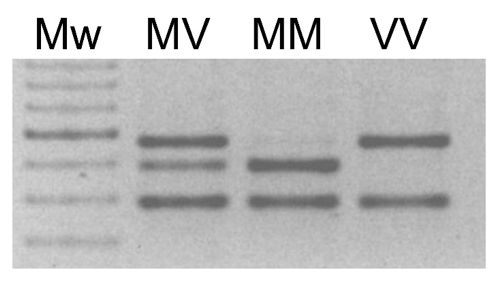
Codon 129: Codon 129 genotyping by PCR amplification of PRNP and restriction enzyme digest with Nsp1. (Mw: 100bp molecular weight ladder (dark band 600bp); MV, MM, VV: codon 129 genotypes)
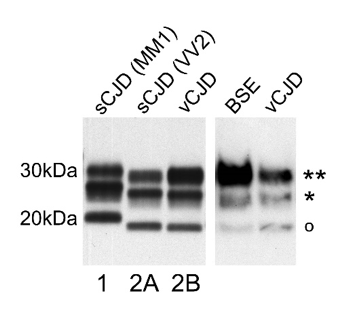
PrPres analysis Western blot image
Detection and typing of abnormal disease-associated prion protein (PrPSc) isoforms by partial proteolytic degradation and Western blot analysis.
Western blot analysis of protease resistant prion protein (PrPres) in post-mortem brain tissue homogenates of cerebral cortex samples from the two most common subtypes of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD MM1 and sCJD VV2), compared with that of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD), and similar analysis of brain stem from a case of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE).
In each example three bands are present, representing non-glycosylated (o), mono-glycosylated (*) and di-glycosylated (**) PrPres. PrPres type 1 differs from type 2 in terms of electrophoretic mobility, most obviously seen by comparing the mobility of the non-glycosylated band. The type 2 PrPres characteristic of vCJD (type 2B) has a predominant diglycosylated band (**), distinguishing it from the type 2 PrPres found in sCJD (type 2A). The predominance of the di-glycosylated band is a feature shared by vCJD and BSE.
The monoclonal antibody 3F4 (which can be obtained from Dako or Signet) is CE marked and was used for the detection and typing of the human specimens shown here. Bovine PrP is not recognised by 3F4, and the vCJD and BSE comparison shown employed the monoclonal antibody 6H4 (from Prionics).
The PrP typing nomenclature is that of Parchi & Gambetti. (Parchi et al., Typing prion isoforms. Nature 1997;386:232-234). The cases of CJD originate from the UK and the Western blot image was provided by Dr. Mark Head (National CJD Research & Surveillance Unit). The BSE tissue was supplied by the Veterinary Laboratory Agency’s TSE Archive (UK) and the Western blot image was provided by Ms Zuzana Krejciova (National CJD Research & Surveillance Unit).